Printing Technologies
Problem:
Given the time and resources necessary to reproduce the complex rime tables by hand, how could those in the Song Dynasty reproduce them in large numbers while keeping costs down?
考虑到手绘复杂的韵表所需要的时间和资源,宋代的工匠们是如何进行韵表的规模生产并控制成本的?
Solution:
Woodblock printing, which first appeared in China around 600 AD, greatly streamlined the mass production of texts and images. The idea was likely inspired by the use of seals and inked rubbings off of stone stele reliefs. This process for block printing on paper was perfected by the end of the Tang Dynasty.
在中国雕版印刷术最早出现于大约公元六百年,这大大加速了文字和图形的批量印刷,这一技术很有可能源自于印章和碑拓技术。在纸张上进行雕版印刷的技术流程在唐代末期臻于完美。
Problem:
每一个木制雕版都由手工雕刻完成,当上面的某一个字脱落或是损毁,将无法进行修复。
Each wooden printing block was hand-carved and when a character broke off or became damaged, it could not be repaired.
Solution:
毕昇(公元990-1051年)发明了活字印刷术。在这之前,如果木制模板上有一个汉字损坏,那么整个模版都要重新刻一遍,这个问题十分常见。有了毕昇的发明,人们只需更换一个活字木块,这极大地提高了印刷的速度降低了成本,同时也让韵表广为流传到广阔的帝国疆域之中甚至之外。
The Movable Woodblock Printing Press was invented by Bi Sheng (990–1051 AD). Before this time, wood plates would need to be re-carved in full each time a character broke (which happened often). With Bi Sheng’s invention, printers only needed to switch out a single block of movable type, which improved the speed and lowered the cost of printing, allowing for a wider circulation of rime tables across the empire and beyond.
Problem:
How do you organize the thousands of Chinese characters needed to create printing plates?
如何对成千上万的汉字来进行排版呢?
Solution:
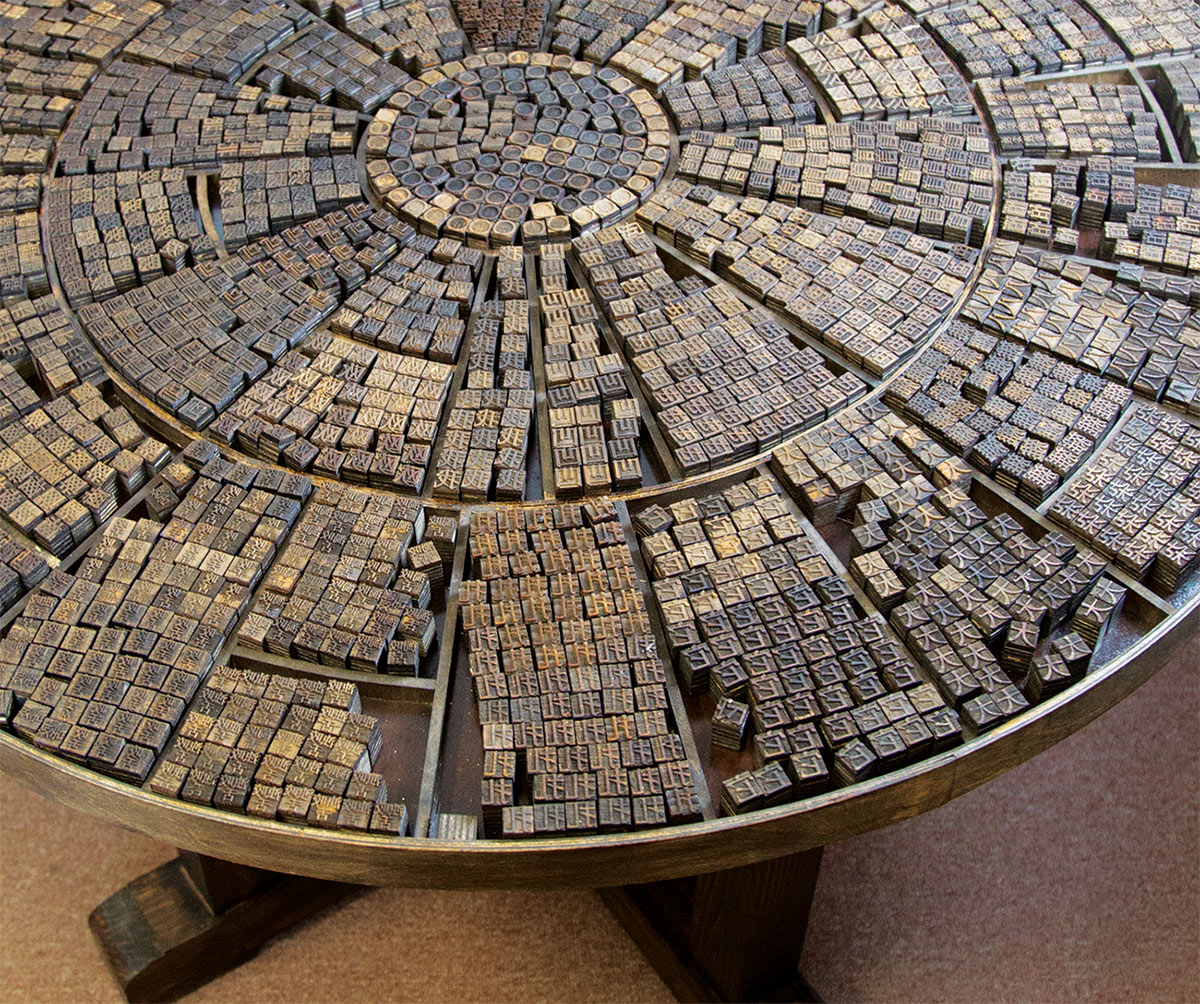
The rotating print case was invented in 1298 AD by Wang Zhen, a Yuan Dynasty government official who organized the characters by their rimes (vowels and tones). A printer could spin and bend the tabletop to select characters more quickly and efficiently. This technology has been adapted in the print case you see here to organize Song Dynasty English into its consonants (outer circle) and vowels (inner circle).
元代官员王祯于1298年发明了轮盘排字法。他根据汉字的韵母(元音和声调)对汉字进行排列。工匠可以通过转动轮盘或倾斜盘身来更快更有效地选择汉字。这一技术在此处的展品中得到改进应用,目的是通过辅音(外圈)和元音(内圈)来对“宋代英语”进行组织排列。